Unraveling the Enigma of the Gut-Brain Axis:
Exploring the Intricate Connection Between Gut Health and Mental Well-Being
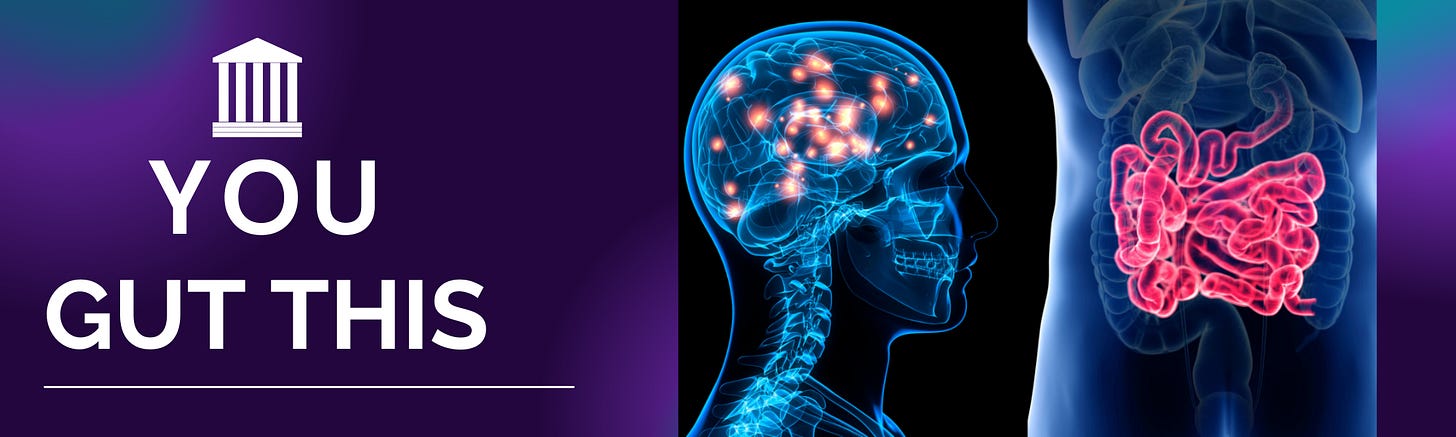
The gut-brain axis, an enigmatic and intricate communication network, facilitates the bidirectional exchange of information between the gut and the brain. Beyond mere intuition and gut feelings, this complex system involves a sophisticated interplay of neurons and chemicals that profoundly impact our cognition, emotions, and behaviors.
The Mighty Gut Microbiome At the core of this captivating interconnection lies the gut microbiome – a thriving community of trillions of microorganisms residing within our digestive tract. Comprising a diverse array of microbes, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, this delicate ecosystem profoundly influences various aspects of our well-being, encompassing digestion, immune function, and brain health.
Gut-Brain Communication Pathways Delving deeper into the mechanisms governing gut-brain communication, we uncover the pivotal role played by neurons lining the gastrointestinal tract, extending from the stomach to the intestines. These enteric neurons transmit signals to specific regions of the brain, triggering the release of neurotransmitters that significantly affect our moods and behaviors. Additionally, the gut microbiome actively generates bioactive compounds that enter the bloodstream, directly influencing brain function and cognitive processes.
The Significance of Gut Health Appreciating the profound link between gut health and overall well-being is paramount to understanding the repercussions of an imbalanced gut microbiome. Dysbiosis, the unhealthy disruption of gut flora, has been linked to a range of health issues, including gastrointestinal disorders, autoimmune conditions, and mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Empowering Gut Health Strategies Armed with knowledge about the gut-brain axis, there are actionable measures we can take to foster a healthy gut microbiome and enhance our overall health. Emphasizing the significance of a gut-friendly diet, we underscore the value of incorporating probiotics, prebiotics, and fiber-rich foods to support beneficial gut bacteria and encourage microbial diversity.
Probiotics: These live microorganisms can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut. Consumption of probiotics helps maintain a healthy balance of gut flora, positively influencing mental health.
Prebiotics: Non-digestible fibers present in foods such as garlic, onions, and bananas serve as nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria, fostering their growth and proliferation.
Fiber-Rich Foods: A diet rich in fiber supports gut motility and enhances the growth of diverse microbial species, contributing to a well-balanced gut ecosystem.
A Glimpse into the Future this article merely scratches the surface; there is a wealth of unexplored territory in the realm of gut microbiome research. In an upcoming article, we will venture even further into this captivating subject. Readers can anticipate gaining profound insights into the complexities of the gut microbiome and acquiring more practical tools to cultivate optimal gut health.
Conclusion: The Health & Wellness experts have illuminated the wonders of the gut-brain axis, unveiling the indispensable role played by the gut microbiome in shaping our physical and mental well-being. Armed with newfound knowledge and actionable guidance, readers are empowered to embrace gut-friendly practices and unlock the full potential of the gut-brain connection for a healthier and more contented life.
FAQs:
Why is the gut-brain axis crucial for our health?
The gut-brain axis facilitates communication between the gut and the brain, impacting our emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. A healthy gut microbiome contributes significantly to overall well-being.
What are some indications of an imbalanced gut microbiome?
Symptoms of an imbalanced gut microbiome encompass digestive issues, frequent infections, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating.
How can I enhance my gut health?
Incorporate probiotics and prebiotics into your diet, consume fiber-rich foods, manage stress, and avoid unnecessary antibiotics.
Can gut health influence mental health?
Indeed, there is a robust connection between gut health and mental well-being. An unhealthy gut microbiome has been associated with conditions like anxiety, depression, and mood disorders.